AndroidX技术栈之性能测试
一般情况下,性能测试主要关注的指标有:CPU、内存占用、电量消耗、GPU、FPS、网络流量、电池温度等等。
CPU性能测试
CPU使用率的获取,当前主要有如下三种方案:
1 基于adb shell dumpsys cpuinfo的方式
命令:adb shell dumpsys cpuinfo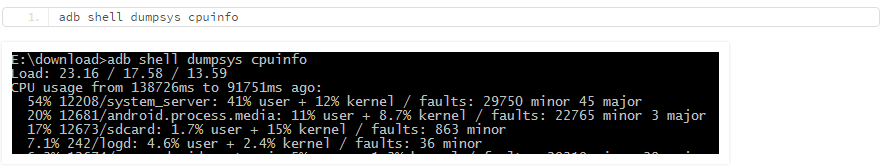 如图可见,从第三行开始,每行表现一个PID对应的CPU使用情况。对应的格式是第一列数据为CPU使用率,第二列为PID/包名, 第三列为对应详细使用率情况。这个方案可以很方便的获取CPU使用率,但是不足的一点是延迟较高,更新较慢。在输出的第二行显示了,当前的cpuinfo数据已经是90秒之前的信息。
如图可见,从第三行开始,每行表现一个PID对应的CPU使用情况。对应的格式是第一列数据为CPU使用率,第二列为PID/包名, 第三列为对应详细使用率情况。这个方案可以很方便的获取CPU使用率,但是不足的一点是延迟较高,更新较慢。在输出的第二行显示了,当前的cpuinfo数据已经是90秒之前的信息。
2 读取/proc/pid/stat的方式
命令:adb shell cat /proc/stat
inux层有公共目录。很多公共信息资源由两个虚拟的文件系统提供:
/proc:包括内存,CPU,网络等
/sys:设备驱动,网络环境(/sys/class/net/)等
通过/proc这个伪文件系统,我们可以和内核内部数据结构进行交互,获取有关进程的有用信息。首先我们可以通过/proc/stat来获取CPU的总体使用情况: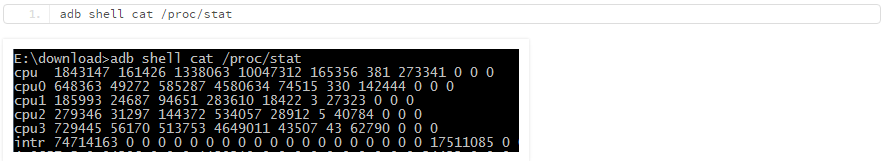 可以看到第一行是CPU的使用情况,后面依次是每个核的使用情况。数据空格隔开,以第一行为例,每列的含义如下:
可以看到第一行是CPU的使用情况,后面依次是每个核的使用情况。数据空格隔开,以第一行为例,每列的含义如下:
cpu:表示名称
user(1843147):从系统启动开始累计到当前时刻,用户态的CPU时间(单位:jiffies) ,不包含nice值为负进程。1 jiffies=0.01秒
nice(161426):从系统启动开始累计到当前时刻,nice值为负的进程所占用的CPU时间(单位:jiffies)
system (1338063) 从系统启动开始累计到当前时刻,核心时间(单位:jiffies)
idle (10047312) 从系统启动开始累计到当前时刻,除硬盘IO等待时间以外其它等待时间(单位:jiffies)
iowait (165356) 从系统启动开始累计到当前时刻,硬盘IO等待时间(单位:jiffies)
irq (381) 从系统启动开始累计到当前时刻,硬中断时间(单位:jiffies)
softirq (273341) 从系统启动开始累计到当前时刻,软中断时间(单位:jiffies)
总的CPU时间 cpu_time = user + system + nice + idle + iowait + irq + softirq
然后,通过如下命令获取单个PID的CPU时间: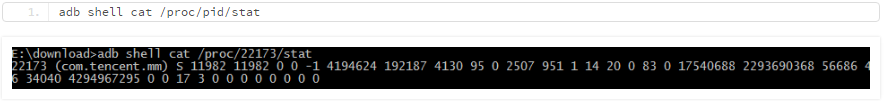
输出中第一列为PID,第14、15列分别为:
utime=2507,该任务在用户态运行的时间,单位为jiffies
stime=951,该任务在核心态运行的时间,单位为jiffies
该PID的CPU时间 pid_cpu_time = utime + stime
因为两次计算的CPU时间都是总量,所以需要每个interval内保存上次的history值,最后得出的CPU使用率为:
CPU% = (pid_cpu_time - old_pid_cpu_time) / (cpu_time - old_cpu_time) * 100%
同样的,想要精确获取CPU使用率,可以通过每个pid对应的数据并累加获得。
这个方案也可以很方便的获取CPU使用率,但是实际中也会发现存在问题:
文件权限,adb shell中获取/proc/pic/stat文件信息时可能会碰到permission deny的情况。
需要依次去获取每个pid数据,一定程度上不能保证时间一致性。
3 基于Linux的top命令
因为Android系统基于的是Linux Kernel,而每个App都是以独立进程的形式运行,所以很自然的想到可以尝试用Linux下的top命令来获取App的CPU使用率。
基本命令为:adb shell top
常用参数一般有如下:
-m:表示需要展示的进程数目
-n:结束前需要刷新多少次
-d:刷新间隔(单位秒)
-s:按照什么列排序(cpu,vss,rss,thr)
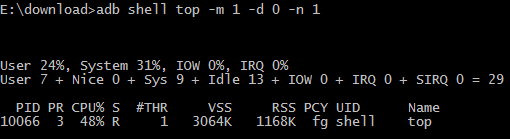
可以看到输出的信息里面主要包括:
PID(进程ID),CPU%(cpu使用率),VSS(虚拟内存使用量),RSS(实际物理内存使用量)等等。
我们一般关心的数据列就是CPU%。
所以我们可以很方便的实现基于TOP获取CPU使用率的方案,伪代码如下:
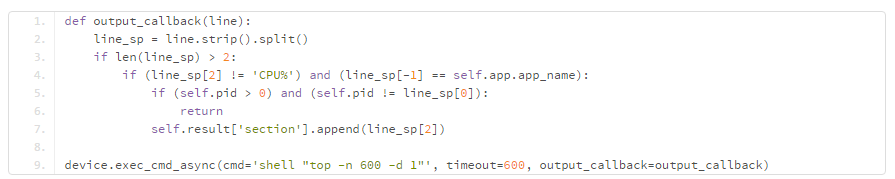
但是实际环境中,我们会发现经常获取到奇怪的数据。
原来在不同的手机上,top命令的输出结构可能会不同,有时候并不是第三列。
所以我们可以先使用如下命令来获取下top的输出格式:
然后根据对应CPU%所在列来获取对应的CPU使用率数据,伪代码如下:
这时,我们已经可以正常的获取到CPU使用率了。
但是根据输出我们会发现,一行数据对于一个PID也就是一个进程,而这样的CPU使用率仅仅为App的主程序的CPU使用率,很多App会存在多进程,如启动一些后台服务,如图为微信的进程信息:
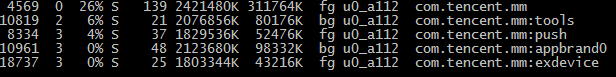
如果需要精确统计App的CPU使用率,其实我们需要将这个App的所有进程的CPU使用率相加。
但是如何获知同属于一个App的所有进程呢?
其实Android对Linux的uid进行了改造,并用于实现App的沙箱机制,每个App对应了一个uid。
对于普通的用户应用,在App安装时,Android就会赋予了一个id即uid,App的所有进程都由这个uid启动。
所以,我们可以根据uid来筛选出同属于一个App的进程,只需要将上述代码增加获取uid列以及uid列的判断即可。
最后,我们只需要定时的去执行获取CPU使用率的函数即可得到CPU性能测试结果。
JAVA代码获取Android手机指定APP的流量/CPU/内存占用信息
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
public class AndroidMonitor {
private static String PID(String PackageName) {
Process proc = null;
String str3 = null;
try {
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
proc = runtime.exec("adb shell ps |grep " + PackageName);
if (proc.waitFor() != 0) {
System.err.println("exit value = " + proc.exitValue());
}
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(proc.getInputStream()));
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
String line = null;
while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) {
stringBuffer.append(line + " ");
}
String str1 = stringBuffer.toString();
String str2 = str1.substring(str1.indexOf(" " + PackageName) - 46, str1.indexOf(" " + PackageName));
String PID = str2.substring(0, 7);
PID = PID.trim();
str3 = PID;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println(e);
} finally {
try {
proc.destroy();
} catch (Exception e2) {
}
}
return str3;
}
public static double getFlow(String PackageName) {
double flow = 0;
try {
String Pid = PID(PackageName);
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
Process proc = runtime.exec("adb shell cat /proc/" + Pid + "/net/dev");
try {
if (proc.waitFor() != 0) {
System.err.println("exit value = " + proc.exitValue());
}
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(proc.getInputStream()));
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
String line = null;
while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) {
stringBuffer.append(line + " ");
}
String str1 = stringBuffer.toString();
String str2 = str1.substring(str1.indexOf("wlan0:"), str1.indexOf("wlan0:") + 90);
String str4 = str2.substring(7, 16);
str4 = str4.trim();
String str6 = str2.substring(67, 75);
str6 = str6.trim();
int b = Integer.parseInt(str4);
int a = Integer.parseInt(str6);
double sendFlow = a / 1024;
double revFlow = b / 1024;
flow = sendFlow + revFlow;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.err.println(e);
} finally {
try {
proc.destroy();
} catch (Exception e2) {
}
}
} catch (Exception StringIndexOutOfBoundsException) {
System.out.println("请检查设备是否连接");
}
return flow;
}
public static double getCPU(String PackageName) {
double Cpu = 0;
try {
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
Process proc = runtime.exec("adb shell top -n 1| grep " + PackageName);
try {
if (proc.waitFor() != 0) {
System.err.println("exit value = " + proc.exitValue());
}
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(proc.getInputStream()));
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
String line = null;
while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) {
stringBuffer.append(line + " ");
}
String str1 = stringBuffer.toString();
String str3 = str1.substring(str1.indexOf(PackageName) - 43, str1.indexOf(PackageName)).trim();
String cpu = str3.substring(0, 2);
cpu = cpu.trim();
Cpu = Double.parseDouble(cpu);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.err.println(e);
} finally {
try {
proc.destroy();
} catch (Exception e2) {
}
}
} catch (Exception StringIndexOutOfBoundsException) {
System.out.println("请检查设备是否连接");
}
return Cpu;
}
public static double getMemory(String PackageName) {
double Heap = 0;
try {
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
Process proc = runtime.exec("adb shell dumpsys meminfo " + PackageName);
try {
if (proc.waitFor() != 0) {
System.err.println("exit value = " + proc.exitValue());
}
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(proc.getInputStream()));
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
String line = null;
while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) {
stringBuffer.append(line + " ");
}
String str1 = stringBuffer.toString();
String str2 = str1.substring(str1.indexOf("Objects") - 60, str1.indexOf("Objects"));
String str3 = str2.substring(0, 10);
str3 = str3.trim();
Heap = Double.parseDouble(str3) / 1024;
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("#.000");
String memory = df.format(Heap);
Heap = Double.parseDouble(memory);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.err.println(e);
} finally {
try {
proc.destroy();
} catch (Exception e2) {
}
}
}
catch (Exception StringIndexOutOfBoundsException) {
System.out.print("请检查设备是否连接");
}
return Heap;
}
}